- 17 Top Diversity Podcasts for 2026 and Beyond - January 16, 2026
- I Tested 4 AI Job Description Rewriters in the GPT Store (and Here’s What I Found) - July 25, 2025
- Why DEI in Canada Relies on Inclusion, Not Quotas - May 16, 2025
Subtle bias in job descriptions is more common than you think. And it deters diverse candidates from applying for your jobs. So what is it?
Subtle bias is hidden. It’s a:
“discrete prejudice or preference toward a certain group, person, or thing that can drive one’s decisions and actions.”
(source: AnnualsReviews.org)
It’s also another word for implicit or unconscious bias.
Understanding Subtle Bias in Job Descriptions
Subtle bias happens when word choice in job listings unintentionally favors a particular gender, age group, or background. Unlike overt discrimination, which is clear and intentional, subtle bias is often hidden in job adverts and goes unnoticed.
This kind of bias can shape the recruitment process. Thus, making it harder for qualified candidates from diverse backgrounds to feel encouraged to apply. Good news—by recognizing these biases, hiring managers can take the first step toward creating inclusive job postings that attract a wider range of candidates.
How Subtle Bias in Job Descriptions Differs from Overt Discrimination
Overt discrimination is obvious. It includes things like stating a specific gender, age, or sexual orientation as a job requirement. Subtle bias, on the other hand, is harder to spot. Therefore, it often appears in job posting descriptions through gendered language, unnecessary requirements, or culture-fit expectations that may exclude people from diverse teams.
For example, common words like “competitive” or “dominant” in job titles may discourage female candidates. While phrases like “energetic” or “recent graduate” might exclude qualified applicants from specific age groups. These may seem like harmless terms, but they can significantly shrink your applicant pool and limit equal opportunities.
The Role of Unconscious Bias in Job Descriptions
Unconscious biases are automatic judgments we make without realizing it. They can influence everything from word choice in job advertisements to the way hiring managers evaluate resumes. Many tech companies, for example, have faced criticism for writing biased language into their job posts. Thus, leading to a lack of diversity in their workforce.
Additionally, using gender-coded words can reinforce gender stereotypes and discourage female applicants from applying. Studies, including academic research published by the American Psychological Association, show that small changes—like using gender-neutral language and removing male stereotypes—can help attract a diverse workforce and create a more inclusive workplace.
Here are 3 examples of subtle bias I find most often when editing job descriptions in Text Analyzer:
1. Subtle Gender Bias
Here’s a job description with 83% masculine-coded words. But, the subtle gender bias in this JD is not the use of masculine words like “Chairman”… it’s the use of “him or her.”
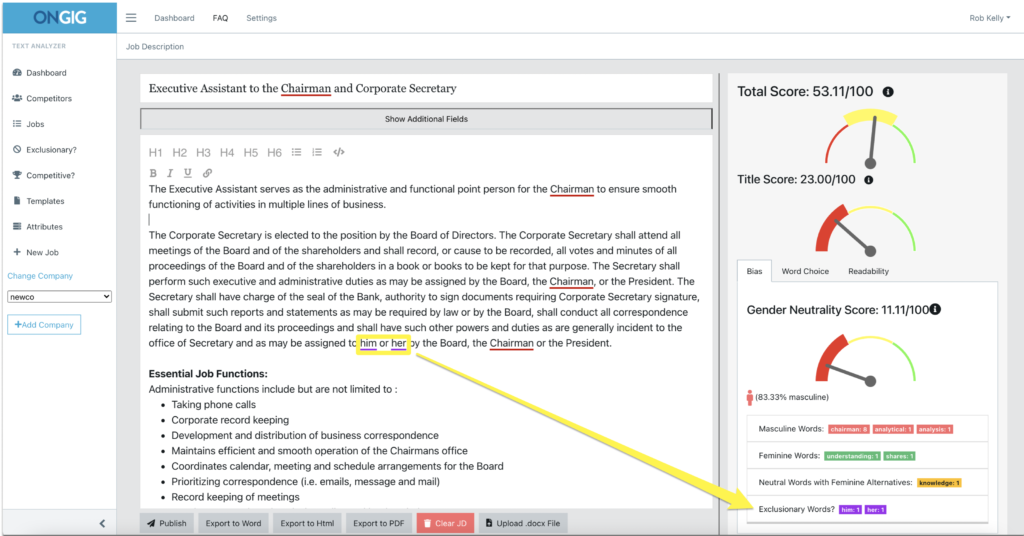
5 to 10 years ago, using “him or her” pronouns was more inclusive than just using “him”.
Today, if you’re only using these pronouns in your JDs…you might be excluding gender non-binary candidates. Or deterring them from applying. “He” or “she” pronouns assume gender identification. And not everyone identifies as male or female.
Tip: Replace gender-coded pronouns with “they,” “them, “you,” or “the candidate” to remove subtle bias from your JDs.
2. Subtle Affinity Bias
Affinity bias is a tendency to prefer candidates who remind us of ourselves. This subtle bias is one to watch out for in your interview process. But subtle affinity bias is present in job descriptions too.
One of the most common examples we see in JDs is the “top school” requirement…aka “elitism bias.”
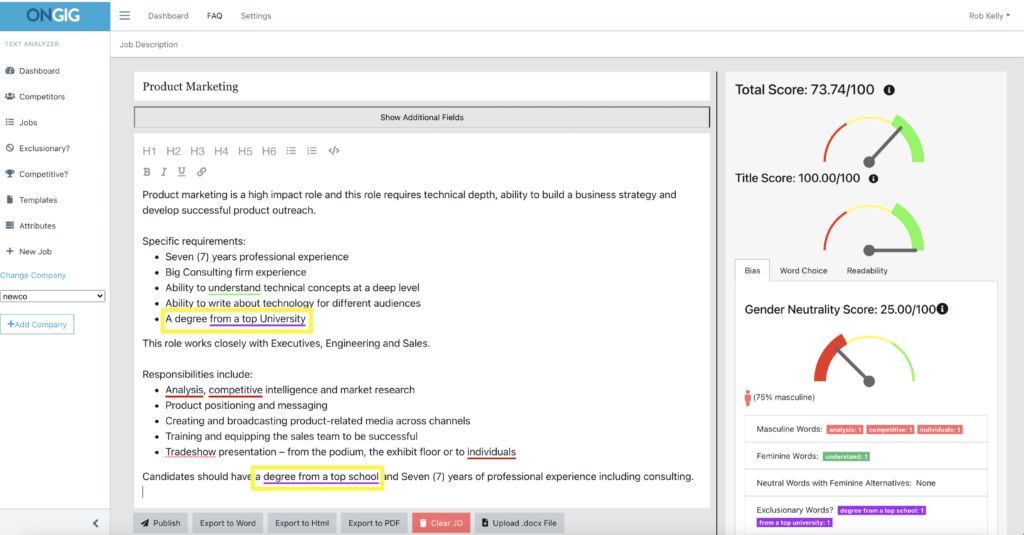
Ongig flags 2 examples of subtle affinity bias in this job ad that might exclude people who didn’t attend a “top school”:
- a degree from a top University
- a degree from a top school
Tip: Replace “top school” language with “a college degree” or name a specific degree that’s required if you want to remove subtle bias from your job ads.
3. Subtle Age Bias
Using words with subtle bias around age makes it more difficult for older people to find new jobs.
“About 58% of workers believe age discrimination begins when they enter their 50s.”
(source: Built In)
This job posting is an example of subtle age bias. The company is looking for a Technical Consultant who is “a digital native.”
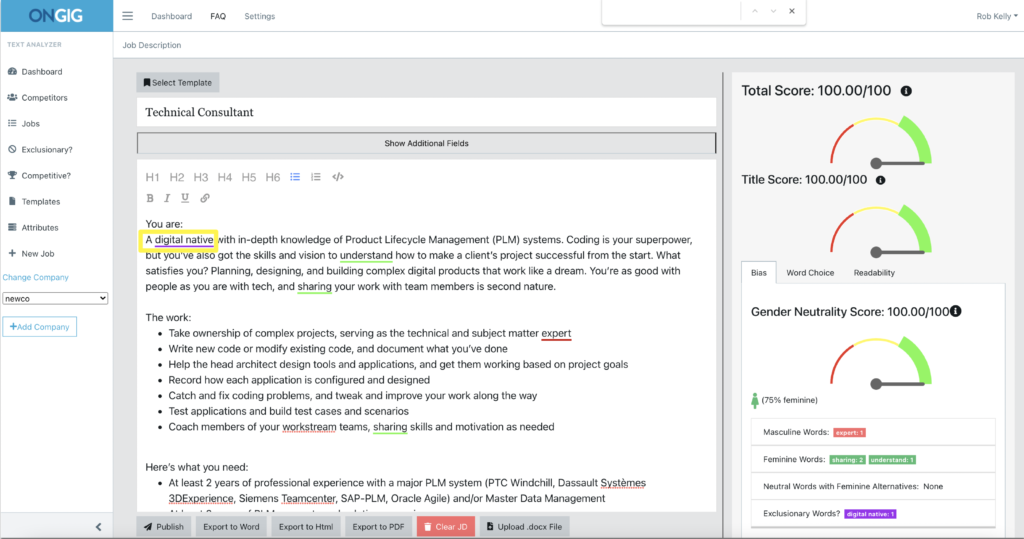
The phrase “digital native” implies a person born (or brought up) during the digital technology age. It might feel exclusionary to older people (and increase your risk of age discrimination lawsuits).
Tip: To remove subtle bias based on age in your JDs, replace words like “digital native” with “person passionate about technology.” You’ll find more examples of age bias (and more inclusive replacements) in our post 6 Ways to Avoid Age Bias in Your Job Descriptions.
The Impact of Subtle Bias in Job Descriptions on the Candidate Pool
Even small biases in job adverts can limit the candidate’s experience and exclude great candidates. So, potential bias in job descriptions can make certain job positions seem like they are meant for people from similar backgrounds, rather than welcoming those with specific skills from diverse talent pools.
Using a gender decoder or text analysis tools is a primary tool to detect red flags in job requirements. So, many companies now use these tools to create unbiased job descriptions that promote equal opportunities and align with the Civil Rights Act.
How to Reduce Subtle Bias in Job Descriptions
Eliminating subtle bias is an important step toward attracting top talent and building a more inclusive workplace. So, here are a few best practices to follow:
- Use neutral titles and avoid gender-coded words.
- Remove unnecessary requirements, like demanding a native English speaker when fluency is sufficient.
- Focus on specific skills rather than years of experience.
- Emphasize work-life balance and a welcoming company culture for diverse talent.
- Use free tools like gender decoders to ensure inclusive language.
Therefore, by making these changes, you can create inclusive job postings that attract qualified candidates from diverse backgrounds, leading to stronger, more innovative teams.
Taking these steps is also a critical step in removing gender biases. Thus, increasing gender equality, and fostering a diverse workforce that reflects a company’s core values.
How Subtle Bias in Job Descriptions Affects the Employer Brand
The Hidden Impact of Biased Language
The words used in a job posting description do more than just list qualifications. They shape how potential candidates view a company. Therefore, if a job ad contains gender roles or suggests a preference for a specific gender identity, it may discourage talented professionals from applying.
Even subtle wording choices can send the wrong message. For example, job ads that use gender-coded language like “dominant” or “nurturing” can reinforce gender inequality. Thus, making some job seekers feel excluded. Over time, this can shrink the talent pool and also make it harder to find the right person for the job.
Bias in Job Descriptions: The Connection Between Language and Reputation
A company’s hiring practices play a pivotal role in shaping its organizational culture. If job ads repeatedly contain biased wording, it can signal a work environment that lacks inclusivity. This doesn’t just affect recruitment. It can also lead to unfair treatment in the workplace and hurt employee retention.
Today’s job market is competitive, and candidates are paying attention. They want to work for companies that value diversity and fairness. Therefore, if they see exclusionary language in a job post, they may assume the company isn’t committed to equal opportunities. And they may also take their skills elsewhere.
Diverse Teams Attract Top Talent
There’s plenty of research showing that diverse teams lead to better innovation, stronger problem-solving, and higher employee satisfaction. So, companies that hire people from different backgrounds build stronger teams and create a more welcoming candidate experience.
Therefore, by removing bias from job descriptions, hiring managers can attract a broader talent pool. This also helps to ensure that you’re reaching the right people for the job. Using a free tool like a bias detector can help identify problematic wording and make job adverts more inclusive.
Removing Bias in Job Descriptions: A Simple Change for a Better Brand
When you prioritize diversity in your hiring process, you send a clear message. It shows that you care about inclusion. This strengthens their reputation, improves culture fit, and also helps you to attract the best talent.
So, for human resources teams and hiring managers, reviewing job descriptions is an important step toward building a diverse, welcoming workplace. Small changes in wording can make a big difference in attracting top candidates. This also helps you with shaping a positive employer brand.
Subtle Bias happens in interviews too
Other subtle bias examples pop up in interviews, not just job ads. Here are a few examples:
- Name bias — bias based on information like a person’s name
- Conformity bias – changing your opinion of a candidate based on the feelings of the rest of the panel
- Beauty bias – choosing candidates based on attractiveness
- Non-verbal bias – bias based on subtle cues like a “weak” handshake
Being aware of these types of subtle bias, and addressing them with your team helps make your overall hiring process more inclusive.
Why I Wrote This?
Ongig’s mission is to create effective and inclusive job descriptions. This includes removing subtle bias from your JDs. Request a demo if you’d like to learn more.
Shout-outs:
- 16 Unconscious Bias Examples and How to Avoid Them in the Workplace (by Bailey Reiners)
- How Subtle Bias Infects the Law (by AnnualReviews.org)
